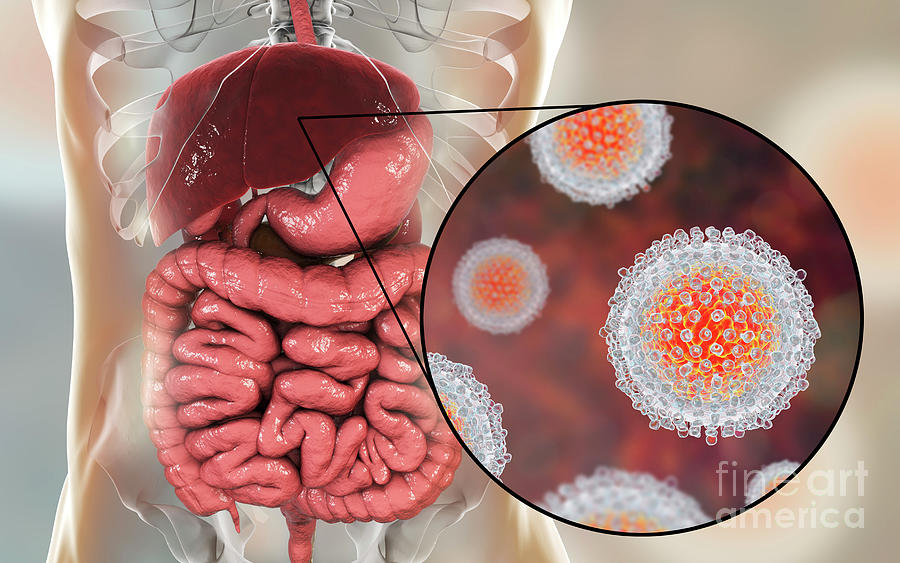
Hepatitis refers to an inflammatory condition of the liver. It’s commonly caused by a viral infection, but there are other possible causes of hepatitis. These include autoimmune hepatitis and hepatitis that occurs as a secondary result of medications, drugs, toxins, and alcohol. Autoimmune hepatitis is a disease that occurs when your body makes antibodies against your liver tissue.
Your liver is located in the right upper area of your abdomen. It performs many critical functions that affect metabolism throughout your body, including:
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 4.4 million Americans are currently living with chronic hepatitis B and C. Many more people don’t even know that they have hepatitis.
Treatment options vary depending on which type of hepatitis you have. You can prevent some forms of hepatitis through immunizations and lifestyle precautions.
The 5 types of viral hepatitis
Causes of noninfectious hepatitis
Common symptoms of hepatitis
If you have infectious forms of hepatitis that are chronic, like hepatitis B and C, you may not have symptoms in the beginning. Symptoms may not occur until the damage affects liver function.
Signs and symptoms of acute hepatitis appear quickly. They include: